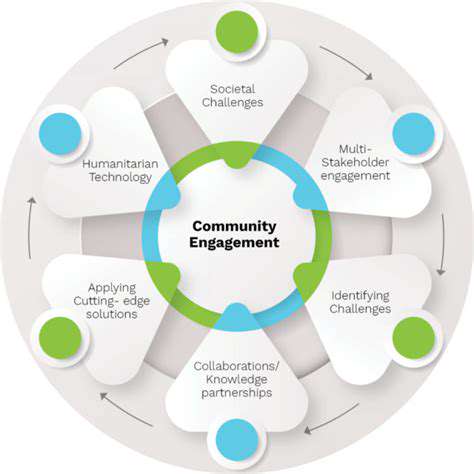
Creative Economics of the Metaverse: New Value Creation
The Importance of Interoperability and Standards

Understanding Interoperability
Interoperability, in its simplest form, refers to the ability of different systems, applications, or devices to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. This seamless exchange is crucial for a multitude of reasons, from streamlining business processes to fostering innovation and collaboration across diverse platforms. Interoperability is becoming increasingly critical in today's interconnected world. It's a fundamental aspect of building robust and adaptable systems that can effectively respond to evolving needs and integrate with emerging technologies.
This concept transcends mere compatibility; it encompasses the ability to understand and interpret data formats, protocols, and standards. Properly designed interoperable systems can significantly reduce the time and resources required for integrating new components or updating existing ones.
Benefits of Interoperable Systems
The advantages of interoperable systems are numerous and far-reaching. Reduced development time and costs are a major benefit, as systems can be more readily integrated and modified. This leads to faster time-to-market for new products and services. Moreover, the enhanced flexibility and adaptability of interoperable systems allow businesses to respond more effectively to changing market demands and emerging technologies.
Furthermore, interoperability fosters collaboration and innovation. Different organizations and departments can easily share data and resources, leading to more efficient workflows and synergy. This collaborative environment empowers organizations to collectively address challenges and innovate in ways not possible with isolated systems.
Technical Aspects of Interoperability
Technical aspects of interoperability encompass a wide range of considerations, including data formats, communication protocols, and application programming interfaces (APIs). Ensuring that data is structured consistently across different systems is a critical component. This involves establishing clear standards and guidelines to define how data should be represented and exchanged. Understanding these technical intricacies is essential for building truly interoperable systems.
Choosing appropriate communication protocols is equally important. This involves selecting protocols that support reliable and secure data transmission between systems. The selection of relevant and robust APIs is also crucial to enable seamless integration between applications.
Challenges in Achieving Interoperability
Despite the numerous benefits, achieving interoperability presents various challenges. One significant challenge is the existence of diverse and often conflicting standards and protocols. Harmonizing these disparate standards can be complex and time-consuming. Furthermore, ensuring data security and privacy across different systems is paramount and can be complicated by varying security policies.
The potential for incompatibility between different systems, applications, or devices is another major concern. Thorough testing and validation are essential to identify and resolve any discrepancies. Thorough documentation and clear guidelines are also essential for effective interoperability.
Real-World Applications of Interoperability
Interoperability has practical applications across numerous industries. In healthcare, interoperable systems allow for the seamless exchange of patient data between different hospitals and clinics, improving patient care and enabling better treatment decisions. In finance, interoperability facilitates the smooth transfer of financial transactions between banks and other financial institutions.
Future Trends in Interoperability
The future of interoperability is characterized by a continued emphasis on standardization and the development of more sophisticated communication protocols. Cloud computing and the rise of the Internet of Things are driving the need for even greater interoperability. The evolution of interoperability will be critical to enabling the next generation of connected systems and services. This is likely to involve an increasing focus on open-source solutions and collaborative development efforts.
Read more about Creative Economics of the Metaverse: New Value Creation
Hot Recommendations
- Immersive Culinary Arts: Exploring Digital Flavors
- The Business of Fan Funded Projects in Entertainment
- Real Time AI Powered Dialogue Generation in Games
- Legal Challenges in User Generated Content Disclaimers
- Fan Fiction to Screenplays: User Driven Adaptation
- The Evolution of User Driven Media into Global Entertainment
- The Ethics of AI in Copyright Protection
- Building Immersive Narratives for Corporate Training
- The Impact of AI on Music Discovery Platforms
- AI for Audience Analytics and Personalized Content