Designing for Universal Access in Immersive Worlds
Navigational Design for Inclusivity
Accessibility Considerations for Navigation
Designing for universal access in immersive worlds necessitates meticulous consideration of navigational elements. Users with diverse abilities, including visual impairments, motor impairments, and cognitive differences, need clear and predictable navigation pathways. This involves employing a range of techniques, such as providing alternative text descriptions for interactive elements, offering multiple input methods (keyboard, voice commands, and assistive technology), and ensuring consistent visual cues for navigation. These considerations are vital to fostering inclusivity and ensuring that all users can effectively explore and engage with the immersive environment.
Furthermore, the design should prioritize predictability and discoverability. Users should be able to easily understand the structure of the environment and locate desired destinations. Clear visual hierarchies, well-labeled interactive objects, and intuitive feedback mechanisms are critical components for fostering a positive user experience for all. This includes incorporating features that allow users to adjust the level of visual complexity and tactile feedback to their specific needs and preferences.
User Interface Design Principles for Diverse Needs
A crucial aspect of navigating immersive worlds for inclusivity involves understanding and adhering to core user interface design principles. These principles encompass the use of clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly technical terminology. The design should also account for cognitive load, ensuring that users are not overwhelmed by an abundance of information or complex interactions. This requires careful consideration of the information architecture, the layout of the interface, and the overall aesthetic presentation. Employing a variety of visual cues, such as color contrast and visual hierarchy, is also essential for users with visual impairments.
Employing a variety of interactive controls, beyond traditional mouse-based interactions, is essential. This includes supporting keyboard navigation, voice commands, and the ability to adjust the level of interaction complexity. Users with motor impairments should have the flexibility to interact with the environment using assistive technologies. Prioritizing universal design principles and accessibility standards ensures that the user interface is usable by a wider range of users, enabling greater participation and engagement in the immersive experience.
Adaptive Navigation and Personalized Experiences
To truly cater to diverse needs, the navigational design should be adaptive and customizable. This means providing users with options to personalize their experience, adjust the level of visual complexity, and tailor the interaction methods to their specific requirements. For example, users with cognitive impairments might benefit from simplified navigation paths or reduced information density. Users with visual impairments might require higher color contrast or alternative input methods. Adaptive navigation allows for a more inclusive experience, allowing individuals to engage with the immersive world in a way that best suits their abilities.
Implementing dynamic navigation options, responsive to user preferences and needs, is crucial. This could involve allowing users to adjust the level of visual complexity, the amount of information presented at once, or the type of feedback given during interactions. Personalization options also enhance the user experience by empowering users to create a tailored environment that aligns with their individual preferences and abilities. This personalized approach fosters a sense of ownership and control, ultimately increasing engagement and enjoyment for all users.
Content Adaptation and Multilingual Support
Content Adaptation Strategies
Content adaptation is a crucial aspect of designing for universal access, ensuring that information is presented in a variety of formats and styles to accommodate diverse user needs and preferences. This includes considering different cognitive abilities, learning styles, and cultural backgrounds. Adapting content might involve providing alternative text descriptions for images, transcripts for audio, and captions for video. Furthermore, employing clear and concise language, avoiding jargon, and using a variety of visual aids, can greatly enhance accessibility for a broader audience.
Effective content adaptation also requires careful consideration of different technological limitations and varying levels of digital literacy. This might involve providing downloadable versions of content or simplified interfaces for users with limited technical proficiency. By implementing robust adaptation strategies, designers can create more inclusive and user-friendly experiences for everyone.
Multilingual Support for Global Reach
Multilingual support is paramount in fostering inclusivity and ensuring global reach. Users from various linguistic backgrounds need access to the same information and resources in their native languages. This requires careful consideration of translation accuracy, cultural nuances, and the potential for misinterpretation. Utilizing professional translators and rigorous quality assurance measures during the translation process is essential to ensure high-quality multilingual content.
Furthermore, implementing robust multilingual support systems can significantly enhance the usability and accessibility of your product or service for a global audience. Designers should consider the linguistic landscape of their target demographic and implement appropriate localization strategies to create a truly inclusive experience.
Accessibility Considerations for Visual Impairments
Visual impairments significantly affect a user's ability to interact with digital content. Designing for universal access necessitates careful consideration of alternative text for images, screen reader compatibility, and sufficient color contrast. These considerations ensure that visually impaired users can perceive and navigate the content effectively.
Providing sufficient color contrast between text and background is crucial for readability. Alternative text descriptions for images and diagrams are essential for conveying the visual information to users who cannot see it directly. Moreover, ensuring screen reader compatibility is vital for users relying on assistive technology to navigate digital content.
Auditory Accessibility and Support for Hearing Impairments
Designing for auditory accessibility is crucial for users with hearing impairments. This includes providing captions for audio and video content, using clear and concise audio cues, and ensuring alternative methods for conveying information. This is critical for ensuring all users can fully engage with the content.
Cognitive Accessibility and Simplified Content
Cognitive accessibility is a critical aspect of universal design, focusing on creating content that is easy to understand and navigate for users with diverse cognitive abilities. This involves using clear and concise language, avoiding jargon, organizing information logically, and providing visual cues and aids. Employing hierarchical structuring, appropriate use of whitespace, and clear labeling of interactive elements can enhance the user experience significantly.
Technical Implementation and Testing
The effective implementation of content adaptation and multilingual support requires rigorous testing to ensure accessibility across various platforms and devices. Thorough testing with assistive technologies like screen readers and captioning software is essential. Regular audits and updates are necessary to maintain compliance with accessibility guidelines and standards. This ensures that your product or service remains accessible and usable for all users, regardless of their specific needs.
The Importance of User Research and Testing

Understanding User Needs
User research is crucial for building successful products and services because it provides critical insights into the needs, desires, and pain points of your target audience. By understanding these factors, you can create products that genuinely meet user expectations and solve their problems effectively. This deep understanding allows developers and designers to build solutions that are not just functional but also intuitive and enjoyable to use.
Failing to conduct thorough user research often results in products that miss the mark and fail to resonate with their intended users. This can lead to wasted resources, lost opportunities, and a negative impact on the overall brand image. Careful consideration of user needs ensures that the final product aligns with actual user requirements, fostering a positive user experience and ultimately leading to greater success.
Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities
A critical part of user research is identifying pain points that users experience while interacting with existing products or services. By understanding these pain points, you can develop innovative solutions that address these issues and provide a more seamless user experience. This process of identifying pain points and exploring opportunities for improvement is essential for continuous development and enhancement of your product or service.
Guiding Design Decisions
User research provides valuable input for informed design decisions. By gathering data directly from users, you can gain insights into their preferences, behaviors, and expectations, which can then be used to create user interfaces and workflows that are more intuitive and effective. This iterative approach ensures that the final design meets the needs of your target audience and enhances the overall user experience.
Thorough user research can prevent costly design mistakes and ensure that the final product aligns with user expectations. By incorporating user feedback at every stage of the design process, you can create a more user-friendly and enjoyable experience.
Measuring Success and Iterating
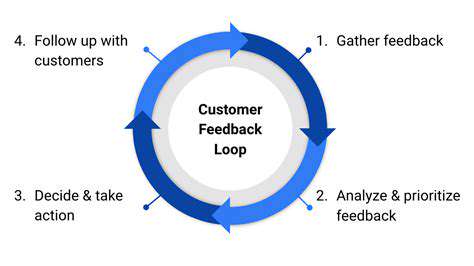
Once a product or service is launched, user research plays a vital role in measuring its success and identifying areas for improvement. By gathering feedback from users, you can determine if the product meets their needs and if there are any areas where the experience can be further enhanced. Collecting and analyzing this feedback allows for data-driven iteration, leading to continuous improvement and refinement of the product or service.
Analyzing user feedback provides valuable insights into how users interact with the product and allows for adjustments to be made in a timely manner. This continuous feedback loop is essential for maintaining a high level of user satisfaction and ensuring that the product remains relevant and effective over time.
Read more about Designing for Universal Access in Immersive Worlds
Hot Recommendations
- Immersive Culinary Arts: Exploring Digital Flavors
- The Business of Fan Funded Projects in Entertainment
- Real Time AI Powered Dialogue Generation in Games
- Legal Challenges in User Generated Content Disclaimers
- Fan Fiction to Screenplays: User Driven Adaptation
- The Evolution of User Driven Media into Global Entertainment
- The Ethics of AI in Copyright Protection
- Building Immersive Narratives for Corporate Training
- The Impact of AI on Music Discovery Platforms
- AI for Audience Analytics and Personalized Content