The Ethics of AI in Predictive Content Creation
Artificial intelligence is transforming content creation in ways we couldn't have imagined a decade ago. Algorithmic storytelling, powered by advanced machine learning models, enables the production of varied content formats - from breaking news updates to customized promotional materials. This automated approach delivers unmatched speed and volume, yet demands serious ethical scrutiny.
The AI-driven content revolution is reshaping our information consumption patterns. The capability to produce massive amounts of personalized content almost instantly creates opportunities for hyper-targeted messaging across industries. While this benefits marketing strategies and educational tools, we must carefully consider potential drawbacks like systemic bias, factual inaccuracies, and the erosion of human connection in communication.
Ethical Implications of Predictive Content Creation
Predictive content generation, a specialized form of algorithmic storytelling, navigates complex ethical waters by forecasting user interests and customizing content delivery. This methodology, though promising for individualized experiences, brings up valid concerns about psychological manipulation and bias amplification. As machine learning models process user behavioral data to anticipate future preferences, they risk creating information bubbles that limit exposure to varied viewpoints.
The ethical use of personal data in these systems demands strict governance frameworks and comprehensive privacy safeguards. Clear disclosure of algorithmic processes and data utilization policies proves essential for establishing user confidence and preventing potential exploitation. Equally important is ensuring these systems don't reinforce existing social prejudices.
Bias and Fairness in Algorithmic Storytelling
One of the most pressing concerns in AI-generated content involves inherent bias. Machine learning models, trained on extensive historical datasets, often unwittingly adopt and magnify societal biases, resulting in content that may disadvantage certain groups. This bias can appear in demographic representation, linguistic choices, and even subject matter selection.
To counter these risks, continuous algorithmic evaluation becomes imperative. Regular independent assessments and data audits help identify and correct biases in training datasets. Involving diverse teams of engineers, ethicists, and content specialists in development processes helps create more inclusive and representative content ecosystems.
The Role of Human Oversight in Algorithmic Storytelling
While AI systems automate numerous content production tasks, human supervision remains indispensable. These technologies should enhance rather than supplant human creativity and discernment. Content editors and quality assurance specialists serve critical functions in maintaining factual accuracy, contextual relevance, and ethical standards in machine-generated material.
Developing comprehensive protocols for human intervention proves essential. This includes establishing clear guidelines about when and how human judgment should inform the content creation workflow. Maintaining this human oversight ensures we balance operational efficiency with ethical content production standards.
Promoting Responsible AI Development
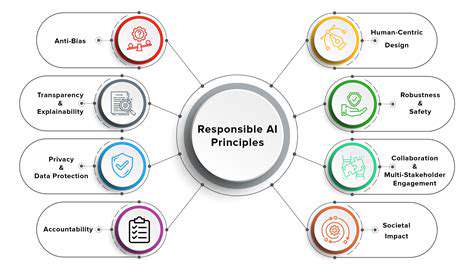
Ethical Considerations in AI Development
Building ethical AI systems requires addressing moral implications throughout the entire development lifecycle. Prioritizing fairness, operational transparency, and system accountability in algorithmic design forms the foundation of responsible innovation. Developers must consciously work to prevent the reinforcement of social prejudices and ensure equitable benefits across all user demographics.
The risk of AI systems inheriting and magnifying human biases, potentially causing unintentional harm, demands proactive ethical safeguards. Particular attention must focus on training data quality, as flawed datasets inevitably produce skewed algorithmic outcomes.
Data Privacy and Security in AI
User data protection stands as a non-negotiable requirement in AI system development. Implementing enterprise-grade security protocols protects sensitive information from cyber threats. This necessitates not just advanced encryption and access management, but also transparent data governance practices aligned with global privacy regulations.
Creating AI solutions that respect privacy while delivering value requires nuanced approaches. Organizations must ensure all data collection and processing activities follow ethical guidelines and comply with relevant data protection laws.
Bias Mitigation and Fairness in AI
Since AI models learn from historical data, they naturally adopt any biases present in that information. Countering this requires careful attention throughout the data pipeline. Bias reduction represents both a technical hurdle and a moral obligation, demanding dedication to equitable treatment of all user groups.
AI developers must implement comprehensive strategies to detect and neutralize biases in both training data and model architectures. Effective approaches include diverse data sampling, fairness-aware model training, and continuous performance monitoring across demographic segments.
Transparency and Explainability in AI
Understanding AI decision-making processes remains critical for establishing user trust and ensuring system accountability. Explainable AI methodologies provide insight into the reasoning behind algorithmic outputs, enabling effective oversight and error detection.
Interpretable AI systems help demystify complex decision pathways, giving users meaningful understanding of the technology powering their experiences.
Accountability and Governance in AI
Clear accountability structures prove essential for responsible AI deployment. This involves defining precise responsibilities for all stakeholders - from engineering teams to regulatory bodies. Effective dispute resolution mechanisms must exist to address any negative impacts.
Comprehensive governance frameworks should guide AI development, integrating ethical principles, legal standards, and societal expectations into every phase of the technology lifecycle.
Societal Impact and Responsible Deployment
AI technologies promise significant social transformation, making thorough impact assessment crucial before deployment. This includes evaluating potential effects on labor markets, economic disparities, and community structures. Proactive stakeholder engagement helps minimize negative consequences while maximizing social benefits.
Understanding the full societal implications of AI systems requires collaborative efforts between technologists and policymakers. This cooperation ensures AI development aligns with broader social welfare objectives and promotes equitable access to technological benefits.