Data Privacy in Metaverse Entertainment Development
Ensuring User Control and Transparency in Data Handling
User-centric Design Principles
One of the most critical factors in maintaining user control involves designing interfaces that feel natural and effortless to navigate. When systems incorporate intuitive layouts and straightforward functionality, users can interact with confidence. Well-crafted instructions and strategically placed guidance eliminate confusion, enabling users to fully leverage the system's capabilities. This approach places the user experience at the forefront, resulting in higher engagement and satisfaction levels.
Systems that offer extensive customization opportunities empower users to adapt the environment to their unique requirements. Detailed control over settings and features gives users the flexibility they need to create personalized experiences that align with their goals.
Transparency in Data Handling
Building trust with users requires complete openness about data practices. People deserve clear explanations about what information gets collected, how it's utilized, and the measures in place to protect it. Comprehensive privacy policies, prominently displayed within the system, form the foundation of this trust. This level of openness not only satisfies regulatory requirements but also strengthens user confidence. Without such transparency, organizations risk damaging relationships and facing legal consequences.
Concrete examples illustrating data usage help users understand practical applications. Breaking down different data types and their specific roles within the system provides clarity and reassurance about information handling.
Control over Data Access and Sharing
Modern systems must provide precise control regarding who can access user data and under what circumstances. Options to limit specific data elements or block automatic sharing with external services should be standard. Sophisticated permission systems play a vital role in protecting sensitive information, giving users peace of mind about their privacy.
The ability to selectively share information with chosen recipients enhances user autonomy. This precision in sharing controls demonstrates respect for user preferences and maintains trust in the system's integrity.
Accountability and Feedback Mechanisms
Establishing reliable channels for user input creates opportunities for continuous system enhancement. Users should have straightforward methods to report issues, suggest improvements, or voice concerns about system behavior. Timely responses to user feedback significantly enhance overall satisfaction. Proactively addressing user needs shows commitment to service quality and fosters long-term loyalty.
Implementing user suggestions through regular updates proves an organization's dedication to improvement. This ongoing refinement process ensures the system evolves in line with user expectations and changing requirements.
Addressing the Challenges of Cross-Platform Data Sharing
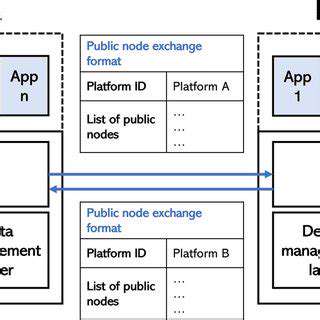
Navigating Cultural Nuances
Effective communication across cultures demands awareness of diverse social norms and traditions. Recognizing these variations prevents misunderstandings that might otherwise occur. Different communication approaches, from direct statements to subtle nonverbal cues, require careful interpretation. Success depends on adjusting one's style to match cultural expectations.
Cultivating cultural awareness demonstrates respect and facilitates smoother interactions. What represents appropriate behavior varies significantly between cultures, making sensitivity crucial.
Overcoming Language Barriers
Language differences present substantial obstacles in international settings. Even when parties share a common language, variations in phrasing, expressions, and pronunciation can lead to confusion. These challenges multiply when working with completely unfamiliar languages.
Bridging Generational Gaps
Age differences introduce additional communication complexities in cross-cultural contexts. Distinct generations often maintain different value systems and communication preferences that can create friction. Understanding historical influences on various age groups helps bridge these divides.
Managing Diverse Perspectives
Successful cross-cultural collaboration requires environments where all voices feel valued. Truly listening to different viewpoints and considering alternative approaches leads to more productive outcomes. Welcoming diverse opinions enriches discussions and decision-making processes.
Approaching differences with empathy acknowledges the validity of varied life experiences. This mindset fosters mutual understanding despite contrasting backgrounds.
Building Trust and Rapport
Establishing meaningful connections across cultures demands time and genuine effort. Consistent, respectful communication and authentic interest in others lay the foundation for strong relationships. Valuing what others contribute strengthens these bonds.
Reliability remains essential for sustaining trust in any cultural context. Keeping promises and following through on commitments demonstrates dependability.
Addressing Potential Conflicts
Cultural differences inevitably lead to occasional misunderstandings. Anticipating areas of potential disagreement helps prevent escalation. Developing resolution strategies that honor cultural variations leads to better outcomes for all parties.
Addressing underlying causes rather than surface symptoms produces lasting solutions. Willingness to find middle ground and communicate openly helps resolve cultural conflicts.
The Role of Ethical Frameworks and Regulatory Initiatives

Ethical Considerations in Data Science
The rapidly advancing field of data science requires strong ethical guidelines to prevent misuse. Professionals must evaluate how their work might affect society, from biased algorithms to privacy breaches. Ethical data collection, analysis, and implementation ensure fairness and minimize potential damage. As technology evolves, maintaining ethical standards becomes increasingly critical.
Ethical data science extends beyond technical execution to encompass broader social implications. The field must address how data practices might reinforce or create social disparities. Addressing these concerns builds public trust in data-driven solutions.
Impact on Algorithmic Bias
Biased data sets can produce discriminatory algorithmic outcomes with real-world consequences. Professionals must rigorously examine their data sources for potential biases. Implementing thorough data screening and continuous algorithm testing reduces discrimination risks. This vigilance helps prevent the automation of existing social inequalities.
Algorithmic bias appears in numerous applications, from financial services to security systems. Identifying and correcting these biases ensures more equitable technological solutions.
The Importance of Data Privacy
In our data-driven era, protecting personal information represents an ethical imperative. Professionals must comply with regulations like GDPR while implementing robust security measures. Data anonymization and secure storage protocols help safeguard sensitive information. Adhering to strict data protection standards prevents breaches and maintains user confidence.
Clear communication about data practices builds essential trust with the public. Transparency about information collection and usage demonstrates respect for individual privacy rights.
Transparency and Accountability
Ethical data science requires openness about methodologies and potential limitations. Detailed documentation of processes enables proper oversight and accountability. Comprehensive records of data sources, analytical methods, and known limitations promote responsible practices. This transparency allows stakeholders to assess work quality and implications.
Establishing accountability structures helps address any negative consequences of data applications. Oversight mechanisms and evaluation processes ensure continued ethical compliance.
Societal Impact and Responsibility
Data science innovations carry significant potential to reshape society in various ways. Professionals must consider how their work might affect different communities and strive for equitable benefits. Anticipating societal consequences helps avoid negative unintended effects. Consulting diverse experts provides valuable perspectives on potential impacts.
Engaging with public concerns demonstrates commitment to responsible innovation. Responsiveness to societal feedback ensures data science applications align with public values and needs. Maintaining open dialogues helps technologies evolve in ways that benefit all members of society.
Read more about Data Privacy in Metaverse Entertainment Development
Hot Recommendations
- Immersive Culinary Arts: Exploring Digital Flavors
- The Business of Fan Funded Projects in Entertainment
- Real Time AI Powered Dialogue Generation in Games
- Legal Challenges in User Generated Content Disclaimers
- Fan Fiction to Screenplays: User Driven Adaptation
- The Evolution of User Driven Media into Global Entertainment
- The Ethics of AI in Copyright Protection
- Building Immersive Narratives for Corporate Training
- The Impact of AI on Music Discovery Platforms
- AI for Audience Analytics and Personalized Content