Building Transparent Moderation Systems for UGC Platforms
Establishing a Multi-Tiered Content Evaluation Framework
Defining the Evaluation Tiers
A well-structured content evaluation framework goes beyond simply adding more reviewers; it requires thoughtful division of responsibilities to guarantee comprehensive and uniform assessment. Each tier must operate with explicit role definitions and evaluation criteria, prioritizing issue escalation based on severity and potential consequences. This structured approach allows for efficient resolution of minor concerns while ensuring complex matters receive appropriate attention.
Developing unambiguous protocols for each evaluation level prevents operational confusion and guarantees that assessors at various stages comprehend their distinct roles within the broader content management system. This precision proves indispensable for upholding both the reliability and uniformity of the evaluation process, which directly impacts user perception of the system's fairness.
Preliminary Content Screening
The foundational layer typically combines automated detection systems with human evaluators conducting initial content scans. This rapid assessment phase serves to immediately identify material violating community standards or presenting substantial risks. This preliminary screening layer proves essential for managing content volume and preventing problematic material from circulating before resolution.
Effective reporting mechanisms form the backbone of this process. These systems should feature intuitive design, easy accessibility, and provide unambiguous explanations for content flags. Such features enable swift identification of potential violations, ensuring subsequent review tiers can address them with maximum efficiency.
Specialized Content Analysis
This evaluation tier typically involves subject matter specialists or veteran moderators conducting in-depth examination of flagged content. These experts analyze context, intent, and potential impact of questionable material, verifying whether initial screening was appropriately targeted or missed critical elements. The specialized review phase ensures nuanced content receives proper consideration, preventing misjudgments and maintaining equilibrium in content management.
This process must incorporate comprehensive documentation of expert reasoning and evaluation criteria. Such documentation becomes crucial for appeal processes and maintaining transparency throughout the content management system.
Dispute Resolution Pathways
A well-designed dispute process is fundamental for establishing trust and demonstrating procedural fairness. Users require clear, navigable channels to contest decisions made at any evaluation stage. This system should remain accessible, comprehensible, and provide opportunities for users to present counter-evidence and perspective, allowing for correction of misunderstandings and demonstration of benign intent.
Distinct escalation protocols are necessary for particularly complex or severe cases. These procedures should explicitly define escalation criteria and identify responsible parties or committees for handling such matters. This ensures significant violations receive appropriate attention while preserving the content management system's integrity.
Continuous Process Improvement
Ongoing training and systematic evaluation of the entire multi-tiered framework are vital for sustaining its efficacy. Moderators require current knowledge and effective tools to perform their duties fairly and efficiently. This includes instruction on community standards, conflict mediation, and content evaluation best practices.
Regular process audits and feedback systems are indispensable for identifying potential weaknesses and implementing necessary enhancements. This cyclical improvement approach guarantees the multi-tiered evaluation framework evolves with changing requirements, maintaining effectiveness over time and fostering a secure, positive digital environment for all participants.
Developing Robust Dispute Resolution Systems
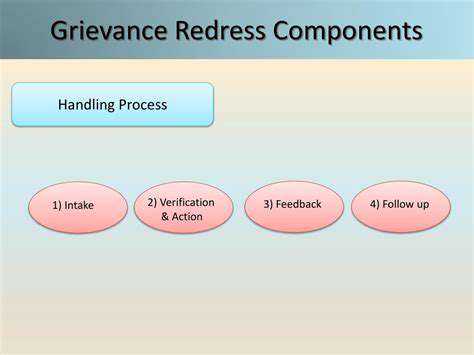
Foundations of Effective Dispute Resolution
Successful dispute resolution systems are built on understanding the psychological principles influencing human decision-making. This requires recognition of diverse motivations and perspectives among decision-makers. Resolution mechanisms should be customized for specific audiences and contexts, addressing individual concerns. This fundamental comprehension ensures dispute processes resonate with participants and improve resolution outcomes.
Moreover, well-structured dispute procedures demonstrate clear understanding of the contested issues. They eliminate ambiguity and present coherent arguments that are easily comprehensible.
Issue Identification and Clarification
The initial phase of effective dispute resolution involves precise definition of the contested matter. This includes identifying core problem elements, scope, and impact on relevant parties. Thorough issue comprehension is prerequisite for developing persuasive and effective resolution strategies.
Constructing Persuasive Arguments
Dispute arguments should maintain logical consistency and substantial evidentiary support. Concrete examples and verifiable data strengthen argument credibility. Providing tangible evidence enhances dispute resolution effectiveness and increases positive outcome likelihood.
Anticipating Counterarguments
Effective dispute resolution anticipates and addresses potential objections. Proactive consideration of opposing views demonstrates comprehensive issue understanding and strengthens overall persuasiveness. By acknowledging alternative perspectives and presenting reasoned responses, dispute processes gain credibility and reduce rejection probability.
Strategic Implementation
Strategic implementation maximizes dispute resolution impact. This requires careful consideration of target audiences and optimal communication channels. Understanding audience communication preferences and priorities is essential for customizing resolution approaches. Timing and delivery method selection significantly influence outcome effectiveness.
Establishing Trust
Building trust and credibility are essential dispute resolution components. Authenticity and transparency foster participant trust. Demonstrating subject matter expertise and genuine concern enhances credibility. Trust and credibility formation are critical for facilitating positive resolution outcomes.
Outcome Evaluation
Comprehensive dispute resolution systems incorporate outcome monitoring and evaluation. Analyzing resolution effectiveness provides valuable insights for process improvement. This analysis enables future process adjustments, ensuring continuous enhancement. This feedback loop optimizes dispute resolution processes and maximizes long-term effectiveness.
Increasing Transparency via Comprehensive Data Analysis
Effective Data Presentation Methods
Data presentation techniques significantly contribute to transparency by transforming complex information into accessible formats. Visual tools like charts and diagrams enable stakeholders to quickly identify important trends and relationships. This simplified representation enhances understanding of underlying information, which is essential for informed decision-making and accountability.
Different presentation methods suit various data types and analytical needs. Bar graphs effectively compare categorical data, while time-series data benefits from line chart presentation. Appropriate method selection maximizes clarity and minimizes misinterpretation. This careful choice ensures data effectively communicates intended messages.
Public Data Accessibility Programs
Public data initiatives promote transparency by making information freely available. This accessibility enables independent analysis and conclusion-drawing by diverse users. Removing data access barriers encourages accountability and public engagement.
Public datasets serve multiple purposes, including government expenditure tracking, environmental monitoring, and community needs assessment. These initiatives significantly contribute to transparent, accountable societies, ultimately strengthening public confidence.
Optimizing Data Accessibility
Ensuring data accessibility constitutes a fundamental transparency component. This involves providing data in formats suitable for diverse users. Clear documentation and user-friendly interfaces substantially improve data comprehension and application. This accessibility benefits all stakeholders regardless of technical expertise.
Data discoverability and retrieval efficiency are equally important. Intuitive search functions, structured metadata, and well-organized datasets facilitate smooth data exploration. These features empower users to quickly locate needed information, further enhancing transparency and accountability.
Enhancing Information Dissemination
Transparent data practices require effective communication channels to share analytical insights. Clear reporting mechanisms are essential for effectively conveying findings to diverse stakeholders. This involves presenting data informatively and engagingly while avoiding technical jargon. Clear communication builds trust and understanding.
Regular performance indicator reporting and trend analysis maintains transparency and accountability. These reports provide clear visibility into progress and challenges. They also facilitate constructive dialogue and feedback mechanisms, further enhancing transparency.
Data Management Frameworks
Comprehensive data governance systems play critical roles in ensuring transparency and maintaining data quality. Establishing clear policies for data collection, storage, and access is essential for maintaining trust. These policies must be transparent and consistently enforced to ensure integrity and prevent misuse. This systematic approach to data management establishes foundations for reliable information.
Adopting standardized data formats and definitions enhances interoperability and usability. Standardization facilitates cross-source and temporal data comparisons. This consistency improves data transparency and reliability, enabling more precise analysis.
Read more about Building Transparent Moderation Systems for UGC Platforms
Hot Recommendations
- Immersive Culinary Arts: Exploring Digital Flavors
- The Business of Fan Funded Projects in Entertainment
- Real Time AI Powered Dialogue Generation in Games
- Legal Challenges in User Generated Content Disclaimers
- Fan Fiction to Screenplays: User Driven Adaptation
- The Evolution of User Driven Media into Global Entertainment
- The Ethics of AI in Copyright Protection
- Building Immersive Narratives for Corporate Training
- The Impact of AI on Music Discovery Platforms
- AI for Audience Analytics and Personalized Content