Building Sustainable Economies in Metaverse Entertainment
Decentralized Models and Tokenized Value
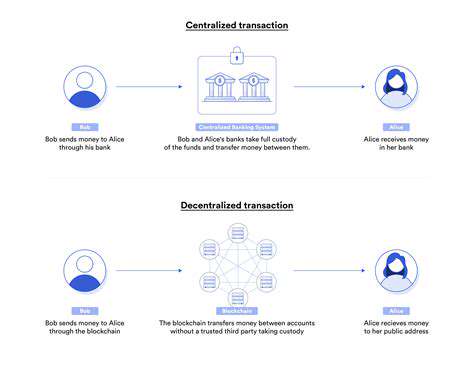
Decentralized Governance Structures
Decentralized models, at their core, aim to distribute power and decision-making authority among a wider group of participants. This contrasts sharply with centralized systems where a single entity holds ultimate control. This shift in power dynamics is crucial for fostering transparency and accountability in various sectors. For instance, in a decentralized social media platform, users, rather than a single company, would have a say in the platform's policies and direction. This empowers individuals and communities.
Implementing decentralized governance requires sophisticated mechanisms for consensus building and dispute resolution. These mechanisms need to be robust enough to handle diverse perspectives and ensure equitable participation, regardless of individual resources or influence. This process can be complex and requires careful design to avoid bottlenecks and ensure smooth operation.
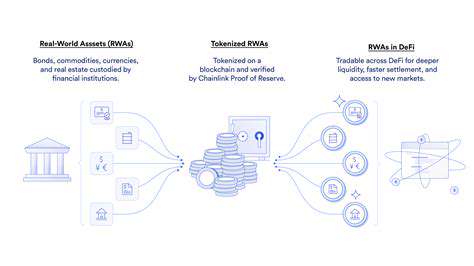
Tokenized Incentives and Rewards
Tokenization plays a crucial role in decentralized systems by creating a system of incentives and rewards. Tokens can represent ownership, access, or participation in a particular network, fostering a sense of community and shared value. For example, in a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform, tokens can grant access to specific services or allow users to vote on platform developments. This creates a direct link between participation and rewards, motivating active engagement.
The use of tokens extends beyond financial applications. In digital communities, tokens can represent contributions, expertise, or unique content, thereby fostering a more active and engaged user base. This incentivizes participation and creates a more dynamic and rewarding environment for contributors.
Security and Scalability Challenges
While decentralized models offer numerous advantages, they also present significant challenges. Security is paramount in any decentralized system, and the complexity of these networks can make them vulnerable to various attacks. Robust security protocols and mechanisms are essential to protect the system and user data from malicious actors. This often requires advanced cryptography and consensus algorithms.
Another key concern is scalability. Decentralized systems, particularly those relying on blockchain technology, can experience performance bottlenecks as the network grows. Optimizing these systems for efficiency and handling increasing transaction volumes is crucial for long-term viability and widespread adoption.
Interoperability and Standardization
Decentralized systems often operate in isolation, hindering seamless interaction between different platforms. Achieving interoperability between various decentralized models is critical for broader adoption and creating a more interconnected ecosystem. Standardization of protocols and data formats is essential to facilitate communication and data exchange across different networks. This will allow for the creation of more complex and integrated applications.
The development of common standards will also enable seamless integration with existing centralized systems. This is crucial for bridging the gap between traditional and decentralized technologies and fostering a more inclusive and collaborative digital landscape.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible Development
Transparency and Openness
Promoting transparency in the development and implementation of sustainable economic models is crucial. This involves clearly outlining the goals, processes, and potential impacts of any initiative, ensuring that stakeholders, including communities and individuals, have access to the information needed to understand and participate in the decision-making process. Transparency fosters trust and allows for accountability, vital elements for building a sustainable and equitable economy.
Open dialogue and collaboration between all relevant parties, from government agencies to private sector actors and community groups, are essential components of this transparency. This includes actively seeking feedback and addressing concerns to create a shared understanding and ownership of the development process, thus minimizing potential conflicts and maximizing positive outcomes.
Equity and Inclusivity
Sustainable economic development must prioritize equity and inclusivity, ensuring that the benefits and opportunities are distributed fairly across all segments of society. This means addressing historical inequalities and actively working to create opportunities for marginalized groups, including women, indigenous populations, and people with disabilities. This requires a deep understanding of the specific needs and challenges faced by these groups and the development of targeted policies and programs to address them.
Ignoring the needs of vulnerable communities can lead to unsustainable economic models that exacerbate existing inequalities and create new forms of disadvantage. A truly sustainable economy considers the well-being of all its members, creating a sense of shared prosperity and opportunity.
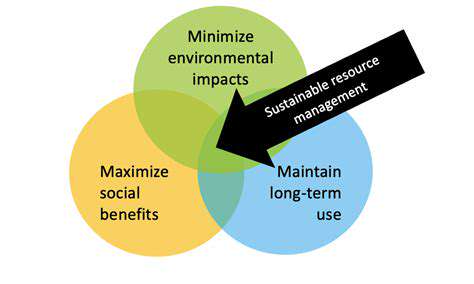
Environmental Impact Assessment
Evaluating the environmental impact of any proposed economic development project is critical. This involves assessing the potential consequences for air and water quality, biodiversity, and natural resources. Thorough environmental impact assessments can help identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies, ensuring that economic growth does not come at the expense of environmental sustainability.
Sustainable solutions require careful consideration of the intricate relationships between economic activities and the environment. A comprehensive approach to environmental impact assessment should inform decision-making, prioritizing solutions that minimize harm and maximize the long-term health of the ecosystem.
Social Responsibility and Well-being
Sustainable economic development should prioritize the well-being of people and communities. This involves creating jobs that provide decent wages and benefits, promoting access to education and healthcare, and fostering a sense of community and social cohesion. These factors are inextricably linked to economic stability and prosperity.
Social responsibility extends beyond the workplace. It includes promoting ethical labor practices, supporting local communities, and ensuring that economic growth is accompanied by improvements in social indicators such as health, education, and safety. A strong social foundation is a crucial element of any sustainable economic model.
Accountability and Governance
Establishing clear mechanisms for accountability and good governance is essential for ensuring that sustainable economic development initiatives are implemented effectively and ethically. This involves establishing transparent decision-making processes, enforcing regulations, and holding individuals and organizations accountable for their actions.
Strong governance structures that promote transparency, participation, and the rule of law are crucial for building trust and fostering a culture of accountability. This is vital for ensuring that sustainable development goals are met and that the benefits of economic progress are shared broadly across society.
Long-Term Vision and Planning
Sustainable economic development requires a long-term vision and strategic planning. Short-term gains should not come at the expense of long-term sustainability. This involves developing comprehensive strategies that consider the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental factors, and that anticipate future challenges and opportunities.
Proactive planning that considers the potential consequences of decisions over decades, rather than just years, is vital. This long-term perspective allows for the development of flexible, adaptable strategies that can respond to evolving circumstances, ensuring that sustainable development initiatives remain relevant and effective over time.
Read more about Building Sustainable Economies in Metaverse Entertainment
Hot Recommendations
- The Future of Audience Participation in the Metaverse
- The Future of Content Distribution: User Driven Models
- Building Immersive Worlds for Social Anxiety Support
- User Generated Educational Resources: Open Learning
- Automated Content Remediation with AI
- How AI Enhances Accessibility for Learning Disabled Audiences
- Immersive Education: Learning Through Engagement
- The Future of Sports Memorabilia: Immersive Digital Assets
- Metaverse Governance: Shaping Entertainment Futures
- Designing for Emotional Response in Immersive Experiences